Since its inception in 2009, Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, has undergone a turbulent journey. From being a niche digital asset to capturing the attention of global investors, regulators, and the general public, Bitcoin has undoubtedly left an indelible mark on the financial landscape. As we stand on the cusp of 2024, the future of Bitcoin and the broader cryptocurrency market remains a subject of intense speculation and analysis.
This comprehensive report from Coinreviews delves deep into the factors shaping the trajectory of Bitcoin in 2024 and beyond. We will explore the key technological advancements, regulatory developments, and macroeconomic trends that are poised to influence the world’s most popular cryptocurrency. By examining historical data, conducting in-depth research, and interviewing industry experts, we aim to provide our readers with a clear and unbiased perspective on the future of Bitcoin.
Whether you’re a seasoned cryptocurrency investor, a curious newcomer to the space, or simply interested in the future of money, this report is a must-read. Join us as we navigate the complexities of the cryptocurrency market and uncover the potential opportunities and challenges that lie ahead for Bitcoin.
What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin (BTC) is a form of cryptocurrency, a digital currency that functions as a decentralized method of payment, independent of any central authority or institution. By eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks or mints in financial transactions, Bitcoin offers a peer-to-peer system for sending and receiving payments securely.
Introduced to the world in 2009 by an anonymous individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin has since grown into the most popular and widely recognized cryptocurrency globally. Its success has led to the creation of numerous other digital currencies.
Continue reading to explore more about Bitcoin—the story of its origins, how to purchase and mine it, and the various ways it can be used today.

Bitcoin has become very popular in recent years.
Main Points
Bitcoin is the result of contributions from multiple innovators, but it is widely accepted that Satoshi Nakamoto launched it in 2008.
Bitcoin operates on a public blockchain, which manages the creation and transfer of its native cryptocurrency, also called Bitcoin.
Bitcoin mining involves competing miners attempting to solve complex computational problems to add a new block to the blockchain, with successful miners earning Bitcoin as a reward.
Bitcoin serves various purposes: speculators and investors use it for investment, while consumers can use it for transactions and exchanges of value.
Despite its potential, Bitcoin comes with risks, including price volatility, fraud, and the possibility of theft.
Who created Bitcoin?
To fully grasp how Bitcoin functions, it’s essential to go back to its origins. The mystery surrounding who created Bitcoin remains intriguing, as more than a decade after its invention, despite extensive research by journalists and the crypto community, the creator’s identity remains unknown.
The foundational principles of Bitcoin were introduced in a white paper published in late 2008 by an individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
While Bitcoin wasn’t the first attempt at creating a digital currency rooted in cryptography and computer science (the paper itself referenced earlier efforts), it presented a distinct and elegant solution to the challenge of establishing trust between online entities, especially in a digital environment where individuals can remain anonymous, much like Bitcoin’s creator, or be located anywhere in the world.
Nakamoto developed two key interlocking ideas: the Bitcoin private key and the blockchain ledger. When you own Bitcoin, you control it through a private key, a unique string of random numbers and letters that unlocks a digital vault containing your Bitcoin. These private keys are recorded and tracked in a distributed ledger known as the blockchain.
Bitcoin’s introduction was a revolutionary breakthrough in computer science, addressing a fundamental issue in online commerce: how to transfer value between two parties without needing a trusted intermediary like a bank. By solving this, Bitcoin has had far-reaching implications. As a currency designed specifically for the Internet, Bitcoin enables financial transactions across borders without involving banks, credit card companies, or even governments. When two individuals, no matter where they are, can exchange value without such intermediaries, it opens up the potential for a more efficient, free, and innovative financial system. In essence, that’s the concept behind Bitcoin.
Understanding Bitcoin in 2024
In August 2008, the domain name Bitcoin.org was registered, marking the early steps of Bitcoin’s development. The site was created by Satoshi Nakamoto and Martti Malmi, who collaborated with the anonymous Nakamoto to help build the foundation of Bitcoin.

Is Bitcoin Easy to Invest in Right Now?
How Bitcoin Started?
In October 2008, Nakamoto introduced the concept of Bitcoin to a cryptography mailing list at metzdowd.com, stating, “I’ve been working on a new electronic cash system that’s fully peer-to-peer, with no trusted third party.” This announcement came alongside the release of a white paper on Bitcoin.org, titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” which has since become the foundational document for understanding how Bitcoin operates today.
First Block
On January 3, 2009, the first-ever Bitcoin block was mined. Known as Block 0 or the genesis block, it contained the message: “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks,” suggesting that the block was mined on or shortly after this date. This marked the official birth of the Bitcoin network.
Rewards
The reward for mining Bitcoin blocks is halved every 210,000 blocks. Initially, the block reward was 50 bitcoins in 2009. On May 11, 2020, the third Bitcoin halving reduced the reward to 6.25 bitcoins. The most recent halving took place in April 2024, lowering the reward to 3.125 bitcoins. The next Bitcoin halving is projected for mid-2028, which will reduce the reward further to 1.5625 BTC.
Denominations
One Bitcoin can be divided down to eight decimal places, with the smallest unit being 0.00000001 Bitcoin, known as a satoshi.
How Does Bitcoins Work?
Unlike credit card networks like Visa or payment platforms like PayPal, Bitcoin isn’t controlled by any single person or organization. Bitcoin is the world’s first fully open payment network, where anyone with an internet connection can participate. It was specifically designed for online use and operates without needing banks or private companies to facilitate transactions.
One of the key elements of Bitcoin is the blockchain, which manages ownership of the currency in much the same way a bank controls assets. However, the significant difference is that Bitcoin’s blockchain is decentralized, meaning anyone can access it, and no single entity has control over it.

How does Bitcoin work?
Here’s a brief overview of how Bitcoin operates:
Specialized computers known as “mining rigs” perform the complex calculations required to verify and log new transactions. In Bitcoin’s early days, standard desktop computers were enough to participate in the mining process, which attracted many individuals to try it. Nowadays, mining requires highly powerful, specialized equipment, often owned by companies or large groups that pool their resources. (By October 2019, mining a single Bitcoin required 12 trillion times more computing power than what was needed when Nakamoto mined the first blocks in 2009.)
The combined computational power of miners ensures the accuracy of the constantly evolving ledger. Bitcoin and the blockchain are intrinsically linked—every newly mined Bitcoin is recorded in the blockchain, as is every transaction made with the existing coins.
How does the Bitcoin network motivate miners to continue performing the vital task of maintaining the blockchain (i.e., verifying transactions)? The network operates as a kind of continuous lottery: mining rigs around the world compete to solve complex mathematical problems. Roughly every 10 minutes, a winner emerges, who then updates the Bitcoin ledger with newly validated transactions. The reward given to these winners has decreased over time. In May 2020, the reward for each successfully mined block dropped from 12.5 bitcoins to 6.25, and after the 2024 halving, it was reduced again to 3.125 bitcoins. This system is designed to ensure the scarcity of Bitcoin.
Initially, a Bitcoin was virtually worthless. By the end of 2019, its value had risen to around $7,500, and by November 2021, it surpassed $64,000. As the value of Bitcoin increased, its divisibility (the ability to buy a fraction of a coin) became an important feature. Currently, one Bitcoin can be divided into eight decimal places (100 millionths of a Bitcoin), with the smallest unit referred to as a Satoshi.
Nakamoto structured the network to ensure that the total supply of Bitcoin would never exceed 21 million, preserving its scarcity. As of December 2023, approximately 1.4 million bitcoins remained to be mined. The last Bitcoin is expected to be mined around the year 2140.
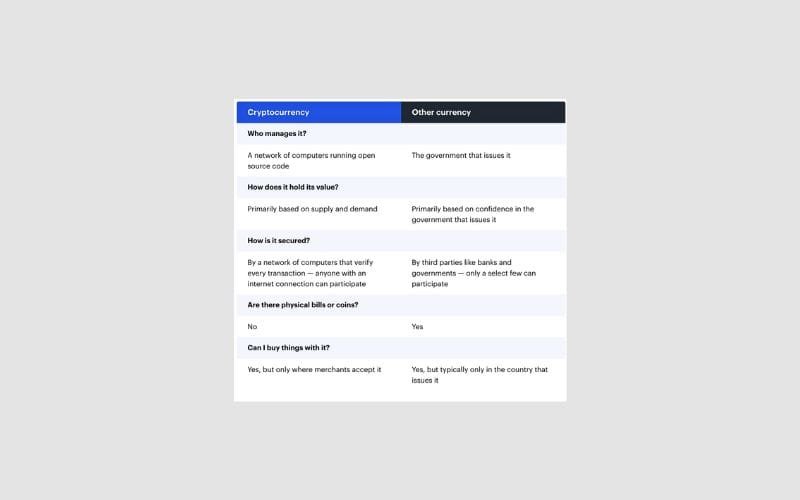
While Bitcoin shares some similarities with traditional currencies—like being used to make purchases or transfer funds electronically—it also has distinct differences. Here are some key points to consider.
Bitcoin’s Blockchain Technology
The concept of Bitcoin as a digital currency is fairly simple to grasp. For instance, if you own a Bitcoin, you can use your cryptocurrency wallet to send smaller amounts of that Bitcoin as payment for goods or services. However, the underlying mechanics of how Bitcoin actually functions are much more complex.
Blockchain
A blockchain is a decentralized ledger—a shared database of information that is linked together using cryptographic methods. “Decentralized” means that the data is stored across many computers, rather than being held on a single centralized server, which is typical in most data storage systems.
The Bitcoin blockchain is maintained by a network of automated programs installed on these computers, performing the essential tasks required for the blockchain to operate.
Each block on the Bitcoin blockchain is a file containing three primary components: the block header, a transaction counter, and the recorded transactions. The transaction counter specifies how many transactions are included in the block, while the block header comprises several important elements:
- Software version: Specifies the version of the blockchain being used (often referred to as the “magic number”).
- Previous block hash: The encrypted data from the previous block.
- Merkle root: A single hash (encrypted data) that represents all the hashed information from previous transactions.
- Timestamp: The exact date and time when the block was created.
- Difficulty target: The current level of difficulty that miners must solve to validate the block.
- Nonce: A “number used once” to solve the mining puzzle and unlock the block.
Each block in the Bitcoin blockchain contains the hash from the previous block, creating a continuous chain of encrypted blocks, which collectively store data from all preceding blocks, tracing back to the very first block of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Encryption
Bitcoin utilizes the SHA-256 hashing algorithm to encrypt (or hash) the data stored in the blockchain’s blocks. In simple terms, transaction data in each block is encrypted into a 256-bit (64-character) hexadecimal number. This number contains all the data from the transactions, as well as information that is tied to all the blocks preceding it.
Brief Fact
Although the data in a block is encrypted and used in subsequent blocks, the information isn’t locked away or unreadable. Each block’s hash is used in the next block, and this
How To Buy Bitcoin in 2024?
If you don’t want to mine Bitcoin, you can purchase it through a cryptocurrency exchange. Given the current price of Bitcoin, most people won’t be able to buy a full BTC, but you can still purchase fractions of one Bitcoin using fiat currencies like U.S. dollars.

Is it easy to buy bitcoin?
For example, on platforms like Coinbase, you can buy Bitcoin by creating an account and funding it through your bank account, credit card, or debit card. This makes buying Bitcoin accessible even in smaller portions.
How To Mine Bitcoin?
Mining Bitcoin requires specialized hardware and software. In the early days of the Bitcoin blockchain, it was possible to mine Bitcoin on a personal computer. However, as Bitcoin gained popularity and more miners joined the network, it became harder for individuals to solve the cryptographic hash and mine successfully.
Although personal computers with newer hardware can still be used to mine Bitcoin, the odds of solving a hash individually are extremely low.
This is because you’re competing with an extensive network of miners generating approximately 600 quintillion hashes per second (as of May 2024). Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) designed specifically for Bitcoin mining can generate over 400 trillion hashes per second, while the latest home computer hardware only manages around 100 megahashes per second.
Options for Successful Bitcoin Mining

Ways to help you mine bitcoin successfully
There are two primary hardware options for mining Bitcoin, along with several software choices:
You can use your existing computer, install Bitcoin-compatible mining software, and join a mining pool. Mining pools are groups of miners who combine their computing power to compete against large ASIC farms. Some of the most well-known mining programs include CGMiner and BFGMiner, while popular pools include Foundry Digital, Antpool, F2Pool, ViaBTC, and Binance.com.
If you have the budget, you can buy an ASIC miner, which is specifically designed for Bitcoin mining. New ASICs typically cost around $10,000, though used ones are also available as miners upgrade their hardware. However, purchasing an ASIC comes with significant expenses, including electricity and cooling, and even owning one or two ASICs doesn’t guarantee mining success, as you’ll be competing with large companies that operate mining farms with thousands of ASICs. For instance, in April 2024, the Bitcoin mining firm CleanSpark ordered 100,000 ASICs from Bitmain.
Tip: Joining a mining pool can increase your chances of earning Bitcoin, but the rewards are shared among pool members. Before choosing a pool, it’s essential to review how they distribute rewards, understand any associated fees, and check user reviews to ensure you’re making the right choice.
How To Use Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was originally created as a peer-to-peer payment system. Over time, its use has expanded beyond that due to its increasing value, competition from other cryptocurrencies, and innovations in blockchains that process data for the Bitcoin network.
Payment
Bitcoin is accepted as a form of payment for various goods and services across many merchants, both online and offline. Physical stores that accept cryptocurrencies typically display signs like “Bitcoin Accepted Here.” Transactions can be conducted using hardware terminals, wallet addresses via QR codes, or touchscreen apps.
For online stores, accepting Bitcoin can be as simple as adding it alongside other payment methods like credit cards or PayPal. To use Bitcoin, you’ll need a cryptocurrency wallet, which serves as your interface with the blockchain. This wallet holds your private keys, which you must enter to authorize Bitcoin transactions.
Investing and Speculating

Bitcoin is very attractive to large investors and speculators.
As Bitcoin gained popularity, it attracted the attention of investors and speculators. From 2009 to 2017, cryptocurrency exchanges emerged, making it easier to buy and sell Bitcoin. Demand steadily grew, and prices began to rise until Bitcoin surpassed $1,000 in 2017.
Many believed that Bitcoin’s value would continue to climb, leading them to buy Bitcoin as a long-term investment. Meanwhile, traders used cryptocurrency exchanges to profit from short-term trades, fueling a dynamic market. After reaching an all-time high of about $69,000 in November 2021, Bitcoin experienced a sharp decline. By March 2022, its price was around $47,454, but it plummeted to $15,731 by November of the same year. Bitcoin later rebounded in 2023, hitting $31,474 before dropping below $30,000 again.
In early 2024, Bitcoin’s price surged into the mid-$40,000s, fueled by growing optimism about the approval of Bitcoin Spot ETFs. By mid-February 2024, after the approval of these ETFs, Bitcoin reached over $50,000.
Bitcoin’s price often mirrors stock market trends, as investors treat it similarly to traditional assets. However, Bitcoin’s price movements are much more volatile, sometimes swinging by thousands of dollars. Many investors engage in “news trading,” responding to major news events, which can cause significant fluctuations in Bitcoin’s value.
Risks of Investing in Bitcoin
Bitcoin experienced significant price fluctuations, starting at $7,167.52 on Dec. 31, 2019, and increasing by over 300% to $28,984.98 a year later. Its upward momentum continued into 2021, reaching an all-time high of $69,000 in November before falling back to around $40,000 in the following months. Due to these dramatic price movements, many people view Bitcoin as an investment asset rather than just a medium of exchange. However, its lack of guaranteed value and purely digital form present several inherent risks.
Numerous warnings from regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) have raised concerns about Bitcoin investing.
Here are some key risks associated with trading or investing in Bitcoin:
- Regulatory Risk: The ongoing legal uncertainties surrounding cryptocurrency-related projects create unpredictability regarding the future liquidity and stability of Bitcoin. While Bitcoin is not classified as a security by authorities as of May 2024, this could potentially change, which adds uncertainty for investors.
- Security Risk: Most people who own Bitcoin acquire it through exchanges rather than mining. Since these exchanges are entirely digital, they are vulnerable to cyberattacks, malware, and operational failures, putting users at risk.
- Insurance Risk: Unlike traditional financial assets, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are not covered by the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC) or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). However, some exchanges, like Gemini and Coinbase, offer insurance for losses resulting from cybersecurity breaches or system failures. Cash deposits on these exchanges may have limited FDIC coverage through “pass-through” insurance.
- Fraud Risk: Despite the secure nature of blockchain technology, Bitcoin is not immune to fraud. Scams and deceptive schemes can still pose threats to users and investors.
- Market Risk: As with any investment, Bitcoin’s value is highly volatile. It has experienced extreme price swings during its existence, and its value is often influenced by high-volume trading and market reactions to significant news events.
Regulating Bitcoin

Does Bitcoin’s price fluctuate frequently?
As with many emerging technologies, regulating Bitcoin has proven challenging. The U.S. government aims to introduce regulations around Bitcoin but faces the delicate task of doing so without stifling an industry that contributes to economic growth.
In the U.S., enforcement agencies continue to apply existing securities, commodities, and tax laws to Bitcoin, yet, as of May 2024, no significant legislative efforts have gained traction in Congress.
Meanwhile, the European Commission introduced its long-awaited Markets in Crypto Assets (MiCA) regulation in 2023, establishing a framework for regulating Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies across the European Union.
In contrast, India took a stricter stance, banning several Bitcoin exchanges in December 2023. The country continues to delay any legislative reviews regarding Bitcoin and other digital currencies.
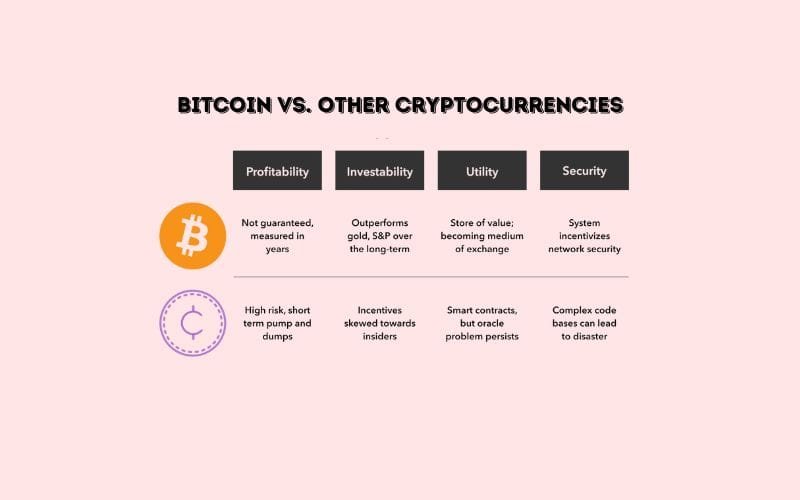
Bitcoin vs. Other Cryptocurrencies
Are Bitcoin vs. Other Cryptocurrencies the Same?
How Bitcoin Compares to Ethereum, Litecoin, and Others?
Bitcoin vs. Ethereum: Bitcoin focuses on being a decentralized digital currency, while Ethereum is a platform for decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Bitcoin’s transaction speed and costs are generally slower and higher compared to Ethereum’s, but Bitcoin’s focus on security and stability sets it apart.
Bitcoin vs. Litecoin: Litecoin was created as a “lighter” version of Bitcoin, with faster transaction times and lower fees. However, Bitcoin’s security and broader adoption give it a significant advantage.
Other Cryptocurrencies: Brief comparison with popular altcoins like Ripple (XRP), Bitcoin Cash, and Cardano in terms of technology, use cases, and adoption.
Pros and Cons of Bitcoin vs. Altcoins
Pros of Bitcoin
- First-mover advantage.
- Highest level of security due to its widespread decentralized network.
- Largest user base and liquidity, making it the most widely accepted cryptocurrency.
Cons of Bitcoin
- Slower transaction speeds and higher fees compared to many altcoins.
- Limited use cases compared to more programmable blockchains like Ethereum.
Why Bitcoin Remains the Most Valuable
- Network effect: Bitcoin has the largest and most decentralized network, making it more secure and harder to manipulate.
- Store of value: Bitcoin is often referred to as “digital gold,” and many investors see it as a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation.
- Institutional Adoption: Bitcoin is the primary cryptocurrency being adopted by large institutions and governments, cementing its place as the most valuable digital asset.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bitcoin

What are the advantages and disadvantages of Bitcoin?
Advantages of Bitcoin
- Decentralization: Bitcoin operates without a central authority or government, making it resistant to censorship and external interference.
- Low Transaction Fees: For cross-border payments, Bitcoin’s transaction fees are often lower than traditional banking fees.
- Inflation Resistance: Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins, ensuring that it cannot be inflated like fiat currencies, which are often subject to government monetary policies.
- Security: Bitcoin’s network is highly secure due to its decentralized nature and the immense amount of computing power used to validate transactions.
- Global Accessibility: Bitcoin can be sent and received anywhere in the world, providing financial inclusion for the unbanked population.
Disadvantages of Bitcoin
- Volatility: Bitcoin’s price fluctuates dramatically, which can make it risky for short-term investors or for using it as a stable currency.
- Scalability Issues: The Bitcoin network can handle a limited number of transactions per second, leading to congestion and higher fees during peak times.
- Energy Consumption: Bitcoin mining requires significant computational power and energy, leading to concerns about its environmental impact.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: In many countries, Bitcoin’s legal status is still unclear, which creates uncertainty for businesses and investors who want to adopt it.
Bitcoin – Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs for Bitcoin
Why Does Bitcoin Exist? Is It Necessary?
Bitcoin exists as a digital currency alternative that isn’t issued by governments or corporations and isn’t controlled by traditional financial intermediaries like banks. Those who see value in Bitcoin include investors, libertarians, individuals facing financial oppression, and others who seek an independent form of money.
Is Bitcoin Legal?
Bitcoin is generally legal to possess in most countries, including all Western democracies where freedom of speech is protected (as Bitcoin is essentially open-source code). Although some countries have made attempts to prohibit the use of Bitcoin, its decentralized nature makes it nearly impossible to enforce complete bans.
Why Does Bitcoin Exist? Is It Necessary?
Bitcoin exists as a digital currency alternative that isn’t issued by governments or corporations and isn’t controlled by traditional financial intermediaries like banks. Those who see value in Bitcoin include investors, libertarians, individuals facing financial oppression, and others who seek an independent form of money.
How Much Is $1 of Bitcoin in US Dollars?
One U.S. dollar’s worth of Bitcoin is equivalent to $1, but the exact amount of Bitcoin that equals $1 changes based on its fluctuating market value.
Is Bitcoin Considered Real Money?
By most standards, money is any item used as a medium of exchange, a store of value, or something that is widely accepted in an economy. Since Bitcoin is used globally for these purposes, it can be regarded as “real money.”
Is Bitcoin a Good Investment?
Bitcoin has a relatively short investment history characterized by highly volatile prices. Whether it constitutes a good investment depends on your financial situation, investment portfolio, risk tolerance, and goals. It’s advisable to consult with a financial professional before investing in cryptocurrency to ensure it aligns with your circumstances.
How Does Bitcoin Make Money?
Miners on the Bitcoin network can earn rewards by successfully opening blocks. Bitcoin can be exchanged for fiat currency through cryptocurrency exchanges, allowing investors and speculators to profit from trading Bitcoin.
How Many Bitcoins Are Left?
As of May 15, 2024, the total number of Bitcoins in existence was approximately 19.7 million, with about 1.3 million remaining to be mined.
How Do I Start Mining Bitcoin?
As Bitcoin has gained popularity and value, the competition for mining rewards has intensified. Most miners now utilize specialized computers specifically designed for mining purposes. This equipment can be costly and requires substantial energy, making the operational expenses a significant barrier for many newcomers.
Consequently, Bitcoin mining presents challenges for beginners. However, some smaller operations opt to join mining pools, where they combine their computational power with others to enhance their chances of earning rewards.
If you’re interested in starting, a good first step would be to research some well-known mining pools and their specific requirements.
Can Bitcoin Be Converted to Cash?
Like many other assets, Bitcoin can be bought and sold for fiat currencies such as the U.S. dollar. The price of Bitcoin will vary depending on current market conditions, which can fluctuate considerably from day to day.
For those looking to buy or sell Bitcoin, there are several options available. For most beginners, the simplest and most convenient method is through a cryptocurrency exchange.
Some exchanges are operated by online stock brokerages, while others are independent. Given the prominence of Bitcoin in the market, it can be traded on nearly any platform that offers cryptocurrency services.
Here are a few additional options for buying and selling Bitcoin:
Peer-to-peer transactions: You may receive Bitcoin as payment for goods or services, or accept it instead of cash.
Bitcoin ATMs: There are over 32,000 Bitcoin ATMs located across the U.S. (You can search Coin ATM Radar to find one near you.)
How to sell Bitcoin?
Just like there are three primary methods for buying Bitcoin, the same options are available for selling Bitcoin: you can use an online exchange platform like Kriptomat, utilize Bitcoin ATMs, or engage with local Bitcoin buyers or online peer-to-peer services.
The Future of Bitcoin

What will the future of Bitcoin be like?
Predictions for Bitcoin’s Price
Historical Price Trends: Overview of Bitcoin’s past price cycles, including notable bull and bear markets, and factors influencing these trends (such as halving events and macroeconomic factors).
Experts’ Predictions: Summarize forecasts from industry experts and analysts, highlighting varying perspectives. Some predict that Bitcoin could reach new all-time highs, potentially exceeding $100,000 per Bitcoin in the coming years, while others caution about the high volatility and possible price corrections.
Factors Influencing Future Prices:
- Institutional Adoption: Increasing involvement of institutional investors (like banks, hedge funds, and corporations) is expected to continue driving demand and price growth.
- Bitcoin Halving: Scheduled halvings every four years reduce the reward for mining Bitcoin, creating scarcity, which typically leads to price increases.
- Macroeconomic Conditions: Global economic instability, inflation, or monetary policy changes can affect Bitcoin’s appeal as a store of value.
Regulatory Considerations
Global Regulations: Governments around the world are still grappling with how to regulate Bitcoin. Some countries like El Salvador have embraced it as legal tender, while others, like China, have imposed stringent restrictions.
Potential Regulatory Scenarios:
- Supportive Regulation: In this scenario, regulators create frameworks that promote Bitcoin’s safe use, foster innovation, and encourage adoption.
- Restrictive Regulation: Some countries may impose heavy restrictions or outright bans due to concerns about illicit activities, market volatility, or loss of control over monetary policy.
- Taxation and Reporting: Increasing regulations regarding taxation and reporting of Bitcoin transactions and holdings could have a significant impact on users and investors.
- Impact of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): The introduction of CBDCs could affect Bitcoin’s role in the financial ecosystem, with potential competition or complementary coexistence.
Bitcoin’s Role in the Future of Digital Finance
- Store of Value (Digital Gold): Many analysts believe Bitcoin will solidify its position as “digital gold,” a safe-haven asset that people turn to during economic uncertainty or inflation.
- Medium of Exchange: While Bitcoin’s use as an everyday currency is limited due to volatility and transaction costs, the development of solutions like the Lightning Network could make Bitcoin a more practical option for payments.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Bitcoin’s integration into decentralized finance could expand its use beyond just a store of value. Bitcoin-backed DeFi applications could offer lending, borrowing, and other financial services.
- Global Financial Inclusion: Bitcoin could play a significant role in bringing financial services to underbanked populations worldwide, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Technological Innovations: Advancements in blockchain technology and the development of second-layer solutions (like Lightning Network) will likely continue to improve Bitcoin’s scalability, usability, and security, making it more relevant for future applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 2024 is poised to be a year of significant growth and development for the cryptocurrency market. From regulatory clarity to technological breakthroughs, the factors shaping the future of Bitcoin and digital currencies are numerous. Coinreviews has provided a comprehensive overview of the key trends and developments that will define this exciting space. By staying informed and making informed decisions, you can position yourself to capitalize on the opportunities presented by this rapidly evolving industry.
Best Crypto Exchange Reviews:
- Binance Review: Features, Supported Cryptos and Fees!
- Bybit Review: Pros, Cons and Key Features
- OKX Review: Pros, Cons, Future Potential & More
- HTX Review: Fees, Security, Pros & Cons
- Bitget Review: Pros & Coins, Fees & More
- Bitfinex Review: Is It Secure or Scam?
- Kucoin Review: Social Trading, Fees, Pros & Cons
- Crypto.com Review: Is the Exchange Safe or Scam?
- BingX Review: Verified Reviews, Pros & Cons
- LBank Review: Should You Use It?
- bitFlyer Review: Pros & Cons and Ratings
- ProBit Review: Is It the Right Crypto Exchange for You?
- P2B Review: Fees, Features, Safety, Pros & Cons
- Pionex Review: Pros, Cons & All You Need to Know
- BitMEX Review: Fees, Trading, Staking & More
- Phemex Review: Is It a Good Crypto Exchange?
- BTSE Review: Is It Safe & Reliable?
- CoinEx Review: Is This Crypto Exchange Safe?
- Poloniex Review: Features, Regulation & Risks
- BITFLEX Review: Features, Safety, Pros & Cons
- CoinJar Review: Is It the Right Exchange for You?
- Paymium Review: Pros, Cons, Key Features & Fees
- LBank Review: Is It the Right Exchange for You?
- MEXC Review: Latest Pros, Cons, Key Features & Fees
- BitMart Review: Reviews, Trading Fees & Cryptos
- Margex Review 2025: Is the Exchange Safe or Scam?
See More: